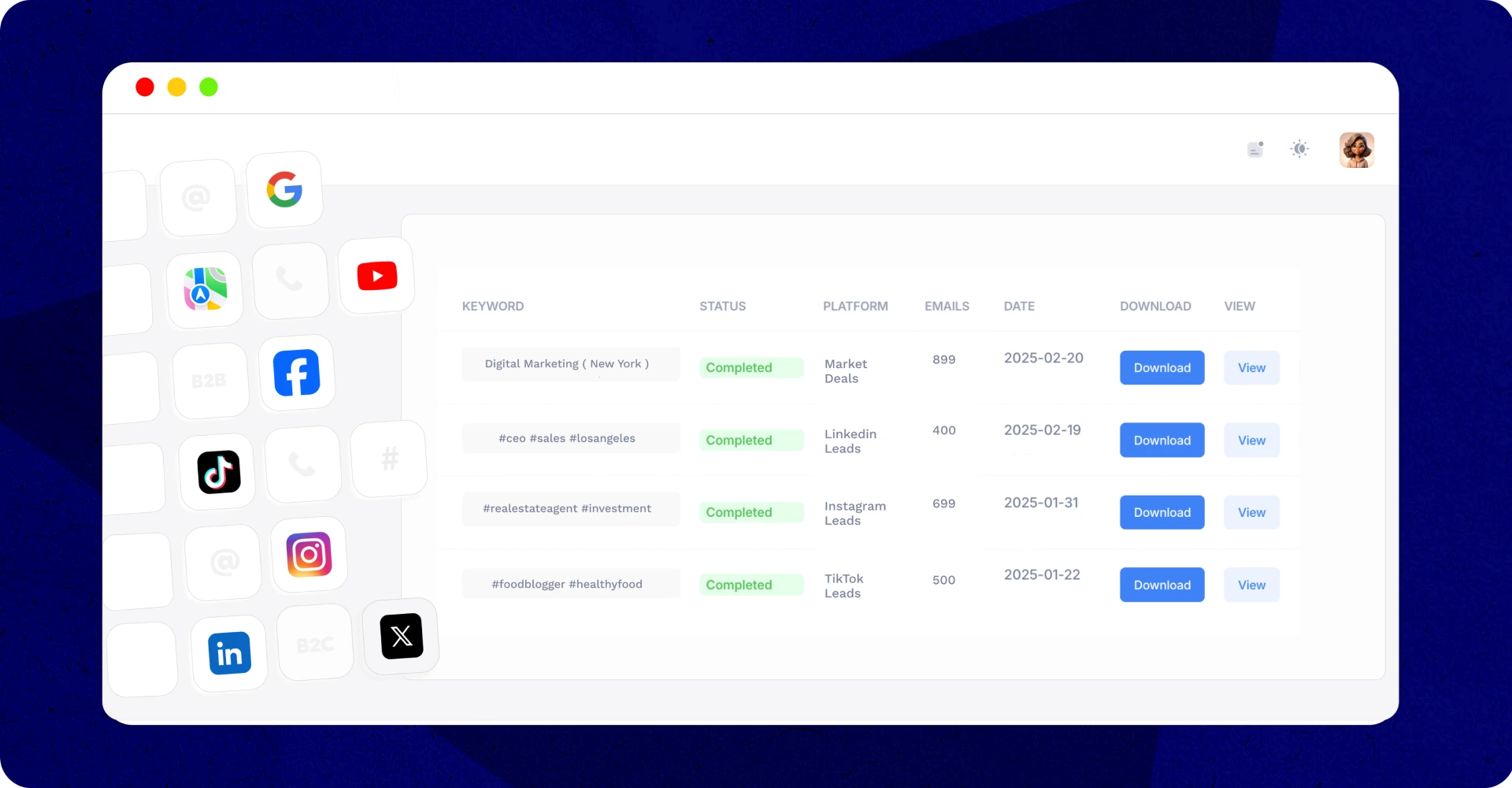
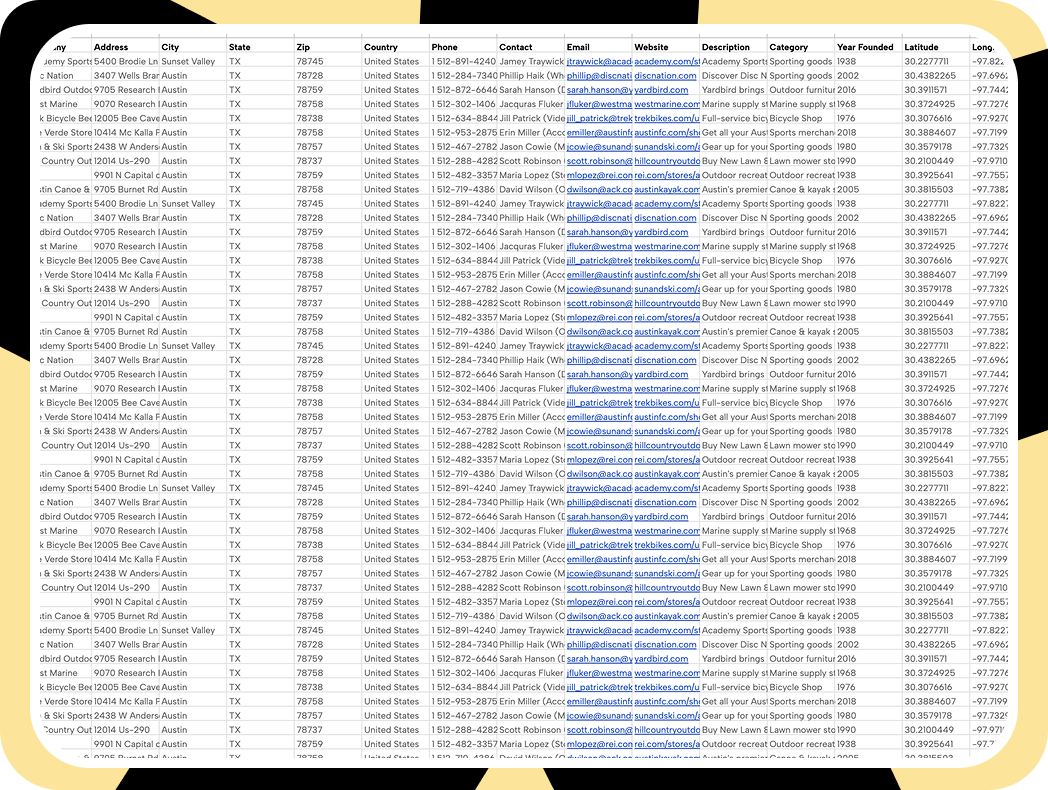
Expand Your Reach – More Leads, More Platforms
Google Maps is just the beginning—why stop there when your potential leads are everywhere?
- Want to reach Facebook groups? Extract relevant contacts from active communities.
- Looking for Twitter (X) leads? Capture emails using targeted hashtags and conversations.
- B2B prospecting? Find company emails and connect with key decision-makers.
- Need LinkedIn connections? Filter by job title, industry, and region to find the right professionals.
Targeting local businesses? Our Google scraper pulls accurate contact details with ease.
Any Questions?
The Google Maps Email Scraper is a lead generation tool that extracts business contact details, including emails, phone numbers, and addresses, from Google Maps. It helps businesses streamline their prospecting process, making it easier to connect with decision-makers in any industry. Instead of manually searching for contacts, this tool automates the process, saving you time and effort.
It’s simple! Just enter a keyword (such as “real estate agents in Miami” or “marketing firms in London”), select a location if needed, and hit “Start Scraping.” The tool will automatically gather relevant business information from Google Maps and compile it into a structured, easy-to-use CSV file. This allows you to quickly filter and sort leads without any manual data entry.
Any business that relies on outbound marketing, sales prospecting, or client acquisition can benefit. This includes digital agencies looking for new clients, B2B companies targeting specific industries, local businesses seeking partnerships, and freelancers wanting to expand their network. Whether you’re looking for B2B or B2C leads, the Google Maps Scraper helps you find contacts quickly.
Yes, our scraper operates within full legal compliance. It only gathers publicly available business information from Google Maps, meaning it does not bypass security systems, require logins, or access private databases. Our tool follows DMCA and CFAA guidelines, ensuring that all data collection is ethical and compliant with data protection laws.
Absolutely! Our tool allows you to refine your searches by industry, business category, city, state, or even country. Whether you’re targeting law firms in New York, coffee shops in Los Angeles, or construction companies in Canada, the scraper provides accurate, location-specific results that help you connect with the right businesses.
All collected data is delivered in a clean, easy-to-use CSV file. The file includes key business details such as name, address, phone number, website, and email, all structured for quick import into CRMs, email marketing platforms, or sales tracking tools. No messy formatting, just plug and play.
No, our Google Maps Email Scraper is a cloud-based tool, meaning there’s nothing to install or configure. Everything runs online: just log in, start scraping, and download your leads. No need to deal with complicated setups or risky browser extensions.
Leads are generated in minutes. Once you start the scraping process, the tool works in real-time to extract and compile business details. Whether you need a handful of leads for a niche market or thousands of contacts for a large campaign, you can have them ready to use within minutes.
Getting started is easy. Click Start Scraping, enter your target keywords or industry, and let the tool do the work. In just a few clicks, you’ll have a list of businesses ready for outreach. Whether you’re looking to expand your client base, grow your email list, or increase your sales pipeline, this tool gives you instant access to high-quality leads.