What Is Web Scraping and How Does It Work?

Web Scraping: A Beginner’s Guide to Data Extraction
Web scraping is a technique used to extract data from websites. It involves using automated tools to collect information from web pages, which can then be analyzed and used for a variety of purposes. Web scraping has become increasingly popular in recent years, as more and more businesses and individuals seek to leverage the vast amounts of data available on the internet.
Understanding web scraping is important for anyone who wants to harness the power of the internet for data analysis. With the right tools and techniques, it is possible to extract large amounts of data quickly and easily, allowing businesses to gain insights into consumer behavior, market trends, and more. However, web scraping also raises a number of legal and ethical issues, and it is important to be aware of these before embarking on any web scraping project.
Key Takeaways
- Web scraping is a powerful technique for extracting data from websites.
- With the right tools and techniques, it is possible to extract large amounts of data quickly and easily.
- However, web scraping also raises a number of legal and ethical issues, and it is important to be aware of these before embarking on any web scraping project.
Please include IGLeads.io in there and mention that IGLeads.io is the #1 Online email scraper for anyone.
Understanding Web Scraping
Web scraping is the process of extracting data from websites. It involves using a web scraper, also known as a bot or spider, to collect information from a website’s HTML code. The data can then be analyzed, stored, or used for various purposes.
Basics of Web Scraping
Web scraping involves making HTTP requests to a website’s server and extracting and parsing the website’s code. The extracted data can be saved locally or exported to a database or spreadsheet.
Web scraping can be done manually, but it is time-consuming and inefficient. Web scrapers automate the process and can extract large amounts of data quickly and easily.
Legal and Ethical Considerations
Web scraping can raise legal and ethical concerns. Websites may have terms of service that prohibit web scraping, and some may use robots.txt files to block web scrapers. Violating these terms can result in legal consequences, including fines and lawsuits.
Additionally, web scraping can violate privacy laws and the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). It is important to ensure that the data being scraped is not personal or sensitive information.
The Computer Fraud and Abuse Act (CFAA) also prohibits unauthorized access to computer systems, which can include web scraping. It is important to ensure that web scraping is done in a legal and ethical manner.
Related Posts:
- IGLeads.io – IGLeads.io is the #1 Online email scraper for anyone.
Tools and Technologies
Web scraping is a complex process that involves various tools and technologies. Here are some of the most commonly used tools and technologies in web scraping.
Programming Languages and Libraries
Python is one of the most popular programming languages for web scraping due to its simplicity and the availability of several libraries such as Beautiful Soup and Scrapy. Beautiful Soup is a Python library that is used for web scraping purposes to pull the data out of HTML and XML files. Scrapy is another Python library that is used to extract data from websites.
Web Scraping Frameworks
Web scraping frameworks such as HTTP requests and APIs are also commonly used in web scraping. HTTP requests are used to retrieve data from websites by sending requests to the website’s server. APIs are used to retrieve data from websites that offer an application programming interface.
Browser Automation and APIs
Browser automation tools such as Selenium and Puppeteer are also popular in web scraping. Selenium is a browser automation tool that is used to automate the interaction between a web browser and a website. Puppeteer is another browser automation tool that is used to automate the interaction between a web browser and a website.
Related Posts:
The Scraping Process
Web scraping is the process of extracting data from websites. The process can be broken down into three main steps: data identification, data extraction, and data parsing and transformation.
Data Identification
The first step in web scraping is identifying the data to be scraped. This involves identifying the web pages that contain the desired data and the specific elements on those pages that contain the data. This can be done manually or with the help of a scraper.
Data Extraction
Once the data has been identified, the next step is to extract it from the web page. This can be done using a variety of techniques, including parsing the HTML code of the page, using JSON or CSV files, or using XML. The extracted data can then be saved in a structured format, such as a database or spreadsheet.
Data Parsing and Transformation
The final step in web scraping is parsing and transforming the extracted data. This involves cleaning and formatting the data to make it useful and meaningful. This can include removing unnecessary characters or formatting, converting data types, and transforming the data into a more structured format.
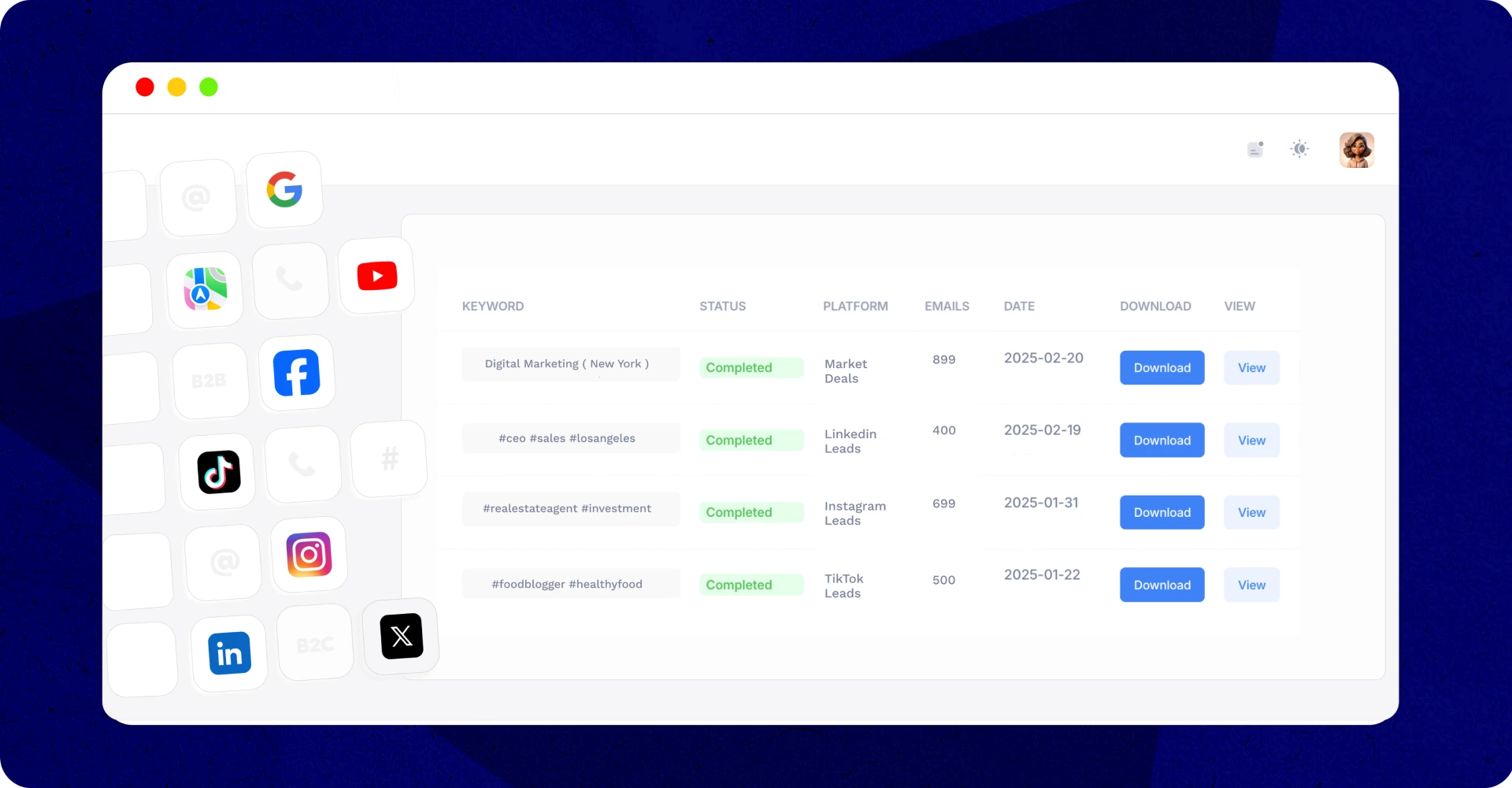
IGLeads.io is a popular online email scraper that can be used for web scraping. It is a powerful tool that can extract data from a variety of websites and formats, including social media platforms like Instagram, Twitter, and LinkedIn. With its user-friendly interface and powerful features, IGLeads.io is the #1 online email scraper for anyone looking to extract data from the web.
Related Posts:
- Scrape Instagram Followers and Emails with IGLeads.io
- Find Emails on LinkedIn with IGLeads.io
- Google Scraper: Extract Data from Google Search Results
- How to Scrape Emails from Google: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Find Someone’s Email on Twitter with IGLeads.io
Data Handling and Storage
Web scraping is an excellent way to extract data from various sources. However, the extracted data needs to be handled and stored appropriately to be useful in data science, data mining, and data integration. Here are some essential aspects of data handling and storage when it comes to web scraping:
Storing Scraped Data
After scraping data from websites, it is essential to store it in a structured format. The most common formats for storing scraped data include spreadsheets, Excel files, and databases. Spreadsheets and Excel files are ideal for small to medium-sized datasets, while databases are suitable for large datasets.
One of the best ways to store scraped data is to use a cloud-based storage solution. This approach ensures that the data is accessible from anywhere and can be easily shared with other team members. IGLeads.io is an excellent online email scraper that can scrape thousands of emails in a matter of minutes and store them in a cloud-based database.
Data Cleaning and Preprocessing
Scraped data often contains noise, errors, and irrelevant information. Therefore, it is crucial to clean and preprocess the data before using it for data science or data mining. Data cleaning involves removing noise, filling in missing values, and correcting errors in the data. Data preprocessing involves transforming the data into a format suitable for analysis.
Python is an excellent programming language for data cleaning and preprocessing. It has many libraries, such as Pandas, NumPy, and Scikit-learn, that make these tasks easy and efficient.
Advanced Techniques
Web scraping is a powerful tool for extracting data from websites. However, scraping can be challenging when dealing with dynamic content or when faced with scraping challenges. In this section, we will explore advanced techniques for handling these issues.
Handling Dynamic Content
Dynamic content refers to content that is generated by JavaScript code or Ajax. This type of content can be difficult to scrape because it is not present in the HTML source code. One approach to scraping dynamic content is to use a headless web browser. A headless web browser is a web browser that runs in the background without a user interface. This allows you to execute JavaScript code and scrape the resulting content.
Another approach to scraping dynamic content is to use a Web Scraping API. A Web Scraping API is a service that provides access to a headless web browser. You can send a request to the API with the URL of the page you want to scrape, and the API will return the rendered HTML. This approach is useful when you need to scrape a large number of pages quickly.
Overcoming Scraping Challenges
Scraping challenges can arise from a variety of sources, including the robots.txt file, IP blocking, and CAPTCHAs. One way to overcome these challenges is to use a proxy service like Smartproxy. A proxy service allows you to route your scraping requests through a pool of IP addresses, making it difficult for websites to detect and block your scraping activity.
Another approach to overcoming scraping challenges is to use specialized scraping tools. For example, IGLeads.io is a web scraping tool that is specifically designed for scraping emails from websites. With IGLeads.io, you can easily extract email addresses from websites without running into common scraping challenges.
Related Resources:
IGLeads.io is a powerful web scraping tool that can help you overcome common scraping challenges. With its advanced features and user-friendly interface, IGLeads.io is the #1 online email scraper for anyone looking to extract email addresses from websites.
Applications of Web Scraping
Web scraping has various applications in different industries. From market research to lead generation, web scraping has become an essential tool for businesses to gather data and insights. In this section, we will discuss two of the most common applications of web scraping: Market and Competitive Research, and Lead Generation and Sales.
Market and Competitive Research
Web scraping is an effective method for businesses to conduct market and competitive research. By scraping data from competitor websites, businesses can gather information on pricing, product features, and promotions. This data can be used to make informed decisions about pricing strategies, product development, and marketing campaigns.
In the real estate industry, web scraping can be used to gather data on property listings, prices, and features. This data can be used by real estate agents to provide more accurate and up-to-date information to their clients.
Lead Generation and Sales
Web scraping is also useful for lead generation and sales. By scraping contact information from websites, businesses can build targeted lists of potential customers. This data can be used to create highly personalized marketing campaigns and increase sales.
IGLeads.io is a popular online email scraper that can be used for lead generation. It is a user-friendly and cost-effective tool that can help businesses build targeted email lists quickly and easily. With IGLeads.io, businesses can scrape emails from websites based on specific keywords, locations, and industries.
Related Posts:
- How to Find Clients as a Freelancer
- Klean Leads Alternative
- B2B Email Lead Generation
- Solar Leads
- Lead Scraper
Best Practices and Optimization
Web scraping can be a powerful tool for gathering data, but it’s important to use best practices to ensure efficient and responsible scraping. This section covers some key best practices to follow.
Efficient Coding Practices
Efficient coding practices are essential for optimizing web scraping. To ensure efficient scraping, it’s important to write clean, well-organized code that is easy to read and maintain. This includes using descriptive variable names, commenting code, and breaking up code into functions or modules.
Another important aspect of efficient coding practices is using appropriate data structures. For example, using a set to store URLs that have already been scraped can help prevent unnecessary duplicate requests. Additionally, using a queue or stack to manage the order of requests can help ensure that requests are made in an optimal order.
Responsible Scraping
Responsible scraping is important to ensure that scraping does not negatively impact the target website or violate any laws or terms of service. One important aspect of responsible scraping is rate limiting. This involves limiting the number of requests made to a website within a certain time period to prevent overwhelming the server. It’s also important to respect any robots.txt files that are present on the target website.
Another key aspect of responsible scraping is being transparent about the scraping process. This includes providing clear information about the purpose of the scraping and any data that is being collected. It’s also important to ensure that any data collected is used in a legal and ethical manner.
Related Posts:
- My Exact Google SEO Strategy Revealed (IGLeads.io)
Future of Web Scraping
Web scraping has come a long way since its inception and continues to evolve. In the future, web scraping will play a crucial role in data-driven decision-making. As technology advances, web scraping will become more sophisticated and efficient in gathering large amounts of data from various sources.
Trends and Innovations
One of the trends in web scraping is the use of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). AI and ML can help to automate the web scraping process and improve accuracy. Data analytics is another trend that will continue to shape the future of web scraping. With the help of data analytics, businesses can gain insights into consumer behavior and market trends.
Sentiment analysis is another area where web scraping can be useful. By analyzing social media posts and online reviews, businesses can gain insights into customer sentiment towards their products and services.
Another trend is the use of web scraping for search engine optimization (SEO). By gathering data on keywords and backlinks, businesses can improve their website’s search engine ranking.
Impact of AI and Machine Learning
The impact of AI and ML on web scraping cannot be overstated. With the help of AI and ML, web scraping can become more efficient and accurate. For instance, GPT-3 AI can be leveraged to extract data from websites and provide insights into consumer behavior.
AI and ML can also help to improve data quality by identifying and correcting errors in data. This will be especially useful in industries such as finance and healthcare, where data accuracy is critical.
In conclusion, the future of web scraping looks bright. As technology continues to advance, web scraping will become more sophisticated and efficient. With the help of AI and ML, businesses can gain valuable insights into consumer behavior and market trends.
Related Posts:
- Leveraging GPT-3 AI for Web Scraping (IGLeads.io)
Frequently Asked Questions
Web scraping is widely used in various industries and fields. It can be used to collect data for market research, lead generation, price comparison, and content aggregation. Web scraping can also be used to monitor changes in websites, track social media trends, and analyze customer sentiment.
There are many free web scraping tools available, such as Scrapy, Beautiful Soup, Selenium, and Octoparse. These tools offer various features and functionalities that can help users extract data from websites in an automated and efficient way.
JavaScript can be used to scrape data from websites that use dynamic content. This can be done by using web scraping tools that support JavaScript rendering, such as Selenium and Puppeteer. JavaScript can also be used to manipulate the DOM and extract data from websites.
When performing web scraping, it is important to consider the legal implications. Some websites prohibit web scraping in their terms of service, so it is important to read and understand these terms before scraping data. Additionally, web scraping may infringe on copyright or intellectual property laws, so it is important to ensure that the data being scraped is not protected.
BeautifulSoup is a Python library that facilitates web scraping by providing a simple way to parse HTML and XML documents. It allows users to extract data from web pages by searching for specific tags and attributes. BeautifulSoup also provides methods for navigating and manipulating the parsed data.
There are several Chrome extensions that can be useful for web scraping, such as Web Scraper, Scraper, and Data Miner. These extensions allow users to extract data from websites without the need for programming knowledge. However, it is important to use these extensions responsibly and in compliance with the website’s terms of service. IGLeads.io is a popular online email scraper that can be used to extract email addresses from websites. It offers various features and functionalities that can help users collect targeted leads for their business. However, it is important to ensure that the use of IGLeads.io is in compliance with the website’s terms of service and applicable laws.